🧪 Definition:
Quantum entanglement is a phenomenon where two or more particles become linked in such a way that the state of one instantly affects the state of the other — no matter how far apart they are.
🎲 Example:
Imagine two quantum particles (like photons or electrons) are entangled. Then:
- You measure the spin of Particle A and find it’s “up.”
- Instantly, you know Particle B’s spin is “down” — even if it’s on the other side of the galaxy.
- This connection exists without any signal traveling between them.
🧠 Albert Einstein called it “spooky action at a distance,” because it seems to defy the speed-of-light limit.
🔍 Key Concepts
1. Superposition + Correlation
- Before measurement, both particles are in a superposition of states (not just one value).
- When one is measured, the other instantly collapses into a correlated state.
2. Not Classical
- This is not like classical twins having matching socks.
- It’s a true quantum connection, beyond any classical explanation or hidden variables (as proven by Bell’s Theorem).
3. No Faster-than-Light Messaging
- While the states are correlated instantly, you can’t send information faster than light using entanglement.
- You still need classical communication to compare results.
🧪 Real-World Applications
✅ Quantum Technologies Using Entanglement:
| Field | Application |
|---|---|
| 🔐 Quantum Cryptography | Unbreakable encryption (Quantum Key Distribution) |
| 🖥️ Quantum Computing | Qubits in entangled states enable massive parallelism |
| 🌐 Quantum Networks | Entangled particles used to connect quantum computers |
| 🎯 Quantum Teleportation | Transfer of quantum states (not matter) via entanglement |
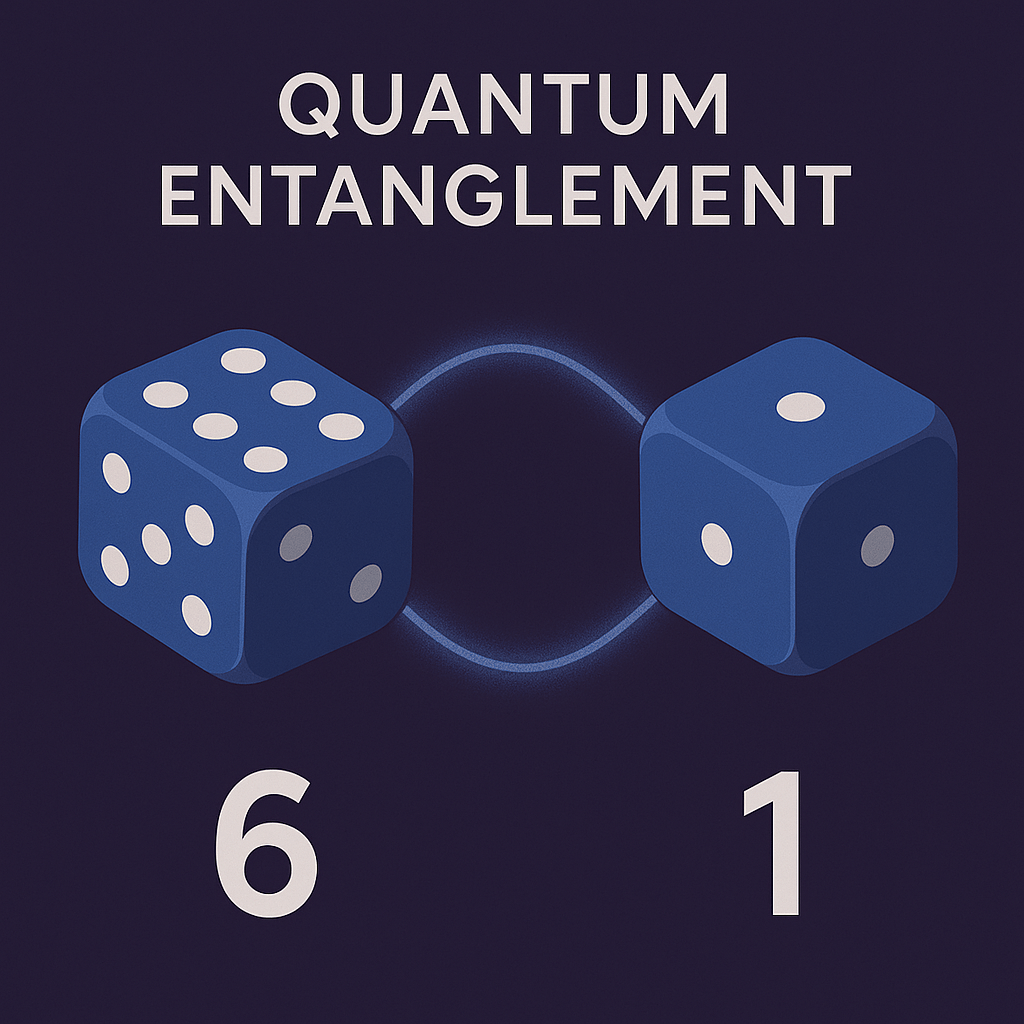
💡 Visual Analogy:
Imagine two dice magically entangled. When you roll one and get a 6, the other instantly shows 1 (always summing to 7), even if it’s in a different universe.
Would you like an image or animation showing this idea?
Leave a comment