Quantum decoherence is the process by which a quantum system loses its “quantumness”—that is, it transitions from behaving like a quantum object (with superpositions, interference, entanglement) to behaving like a classical object we see in daily life.
🌟 Imagine This:
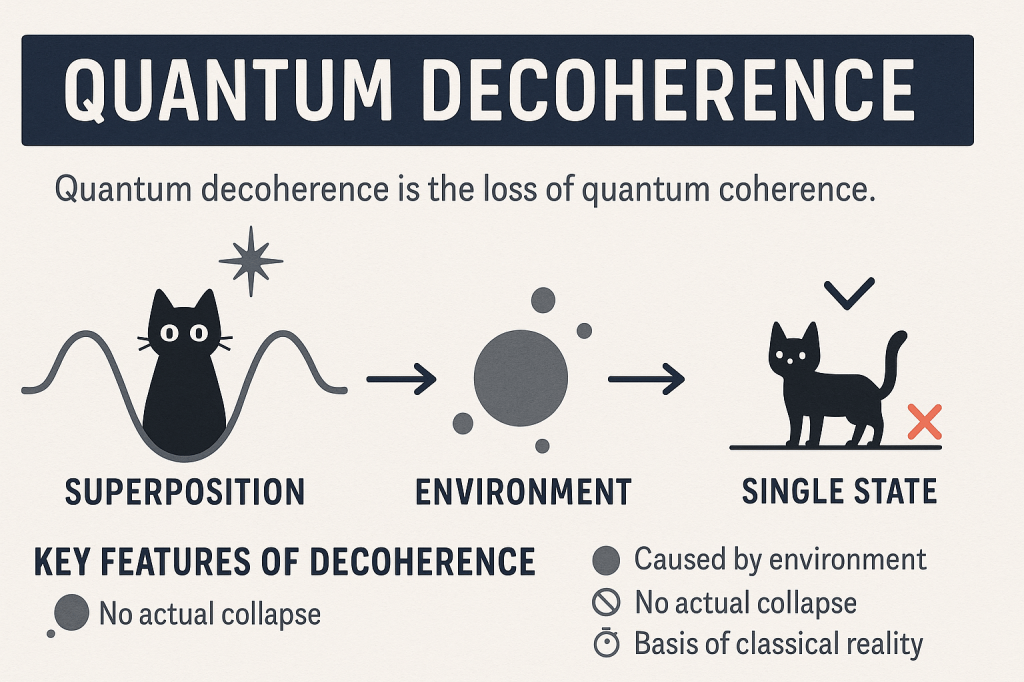
In quantum mechanics, a particle can exist in a superposition—being in multiple states at once (like Schrödinger’s cat being both dead and alive).
But in real life, we never observe such weird states. Why?
🎭 Decoherence Explains the Collapse (Sort of…)
When a quantum system interacts with its environment (like air, light, atoms nearby), this interaction causes the delicate superposition to “leak” into the environment.
The quantum information gets spread out and becomes practically impossible to retrieve.
The system looks like it has “chosen” a single state.
🔬 Key Features of Decoherence:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Caused by environment | Even tiny interactions ruin superpositions. |
| No actual collapse | It’s not about a particle deciding a state—it’s about information becoming inaccessible. |
| Very fast | Happens on incredibly short time scales (nanoseconds or faster). |
| Basis of classical reality | Explains why the world around us doesn’t look quantum. |
🌀 Decoherence ≠ Wavefunction Collapse
- Decoherence: Mathematical process from entangling with environment.
- Collapse: Postulated in standard quantum mechanics when a measurement is made.
Decoherence makes collapse appear to happen—without needing to “break” quantum rules.
📦 Real-World Implications
- Quantum computing: Decoherence is the biggest enemy—it destroys qubits.
- Quantum biology: Some biological processes seem to avoid decoherence for a while.
- Many-worlds interpretation: In this view, decoherence causes branching into alternate outcomes without true collapse.
Leave a comment