Most wonderful Properties of Light
🌈 1. Properties of Light
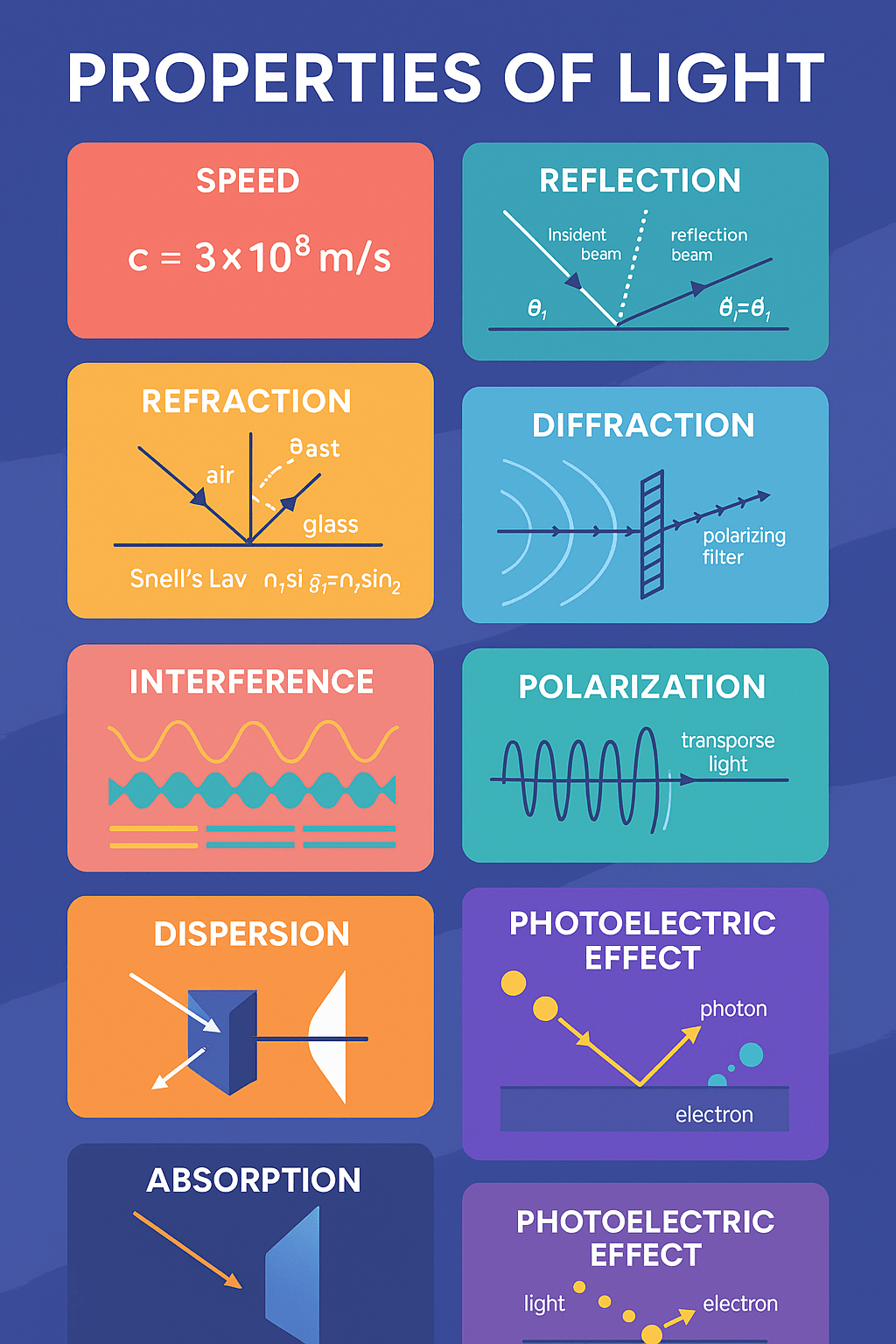
Light is a form of energy that travels as an electromagnetic wave but also behaves like particles (photons). Here are its key properties:
✔ Speed
- In vacuum: 3 × 10⁸ m/s
- Slows down in water, glass, etc.
✔ Reflection
- Bouncing of light off a surface.
- Law: Angle of incidence = angle of reflection
- Example: Mirrors.
✔ Refraction
- Bending of light when it passes from one medium to another.
- Caused by a change in light’s speed.
- Example: A straw looks bent in water.
✔ Diffraction
- Light spreads out when it passes through a narrow slit.
- More noticeable with small slits or obstacles.
✔ Interference
- Overlapping light waves produce bright and dark patterns.
- Seen in thin films like soap bubbles.
✔ Polarization
- Filters light to vibrate in one direction only.
- Used in sunglasses and LCD screens.
✔ Dispersion
- Splitting of white light into its color components (spectrum).
- Example: Rainbow, prism.
✔ Absorption & Transmission
- Materials may block, absorb, or allow light.
- Transparent: light passes through (glass)
- Translucent: partial transmission (frosted glass)
- Opaque: blocks light (wood)
✔ Photoelectric Effect
- Light hits a metal → ejects electrons.
- Shows that light behaves as particles (photons).
- Einstein won the Nobel Prize for this!
🔄 2. Can We Bend Light?
Yes, light can change direction under certain conditions — though not like bending a wire!
🌊 A. Refraction
- Most common method.
- Light bends when entering a medium with different density.
- Applications: Lenses, eyeglasses, magnifying glasses.
🌠 B. Gravitational Bending
- Predicted by Einstein.
- Massive objects bend spacetime, and light follows the curve.
- Known as gravitational lensing (see below).
🔍 C. Prisms and Lenses
- Prisms split and bend light (dispersion).
- Lenses focus or spread light.
🌅 D. Atmospheric Bending
- Light bends due to air layers of different temperatures.
- Examples: Mirages, flattened Sun at sunset.
🌌 3. Gravitational Lensing
Gravitational lensing is a powerful effect of Einstein’s General Relativity.
🌀 What Happens?
When light from a distant galaxy passes near a massive object (like a black hole or galaxy cluster), the object’s gravity bends the light.
- Acts like a cosmic magnifying glass.
- Helps us observe distant galaxies or objects hidden behind other ones.
🧭 Types of Gravitational Lensing:
| Type | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Strong Lensing | Creates arcs, rings (Einstein rings), multiple images | Seen in Hubble images |
| Weak Lensing | Slight distortion in galaxy shapes | Used in dark matter mapping |
| Microlensing | Temporary brightening as a star passes in front of another | Detects exoplanets |
🌠 Why It’s Important:
- Confirms Einstein’s theory.
- Maps dark matter (which doesn’t emit light).
- Reveals early and distant galaxies.
🕳️ 4. What is Dark Matter?
Dark matter is an invisible form of matter that makes up about 27% of the universe.
🕵️♂️ We Can’t See It, But We Know It’s There!
Evidence for dark matter comes from:
🔄 Galaxy Rotation
- Galaxies rotate too fast to be held together by visible matter alone.
- Invisible “extra mass” is holding them in.
🔭 Gravitational Lensing
- Light bends more than expected → hidden mass is present.
🌌 Structure Formation
- The way galaxies formed after the Big Bang needs dark matter to explain it.
🤔 What Could It Be?
Dark matter is probably made of unknown particles like:
- WIMPs (Weakly Interacting Massive Particles)
- Axions
- Sterile Neutrinos
It is not:
- Normal atoms
- Black holes
- Ordinary gas
- Antimatter
📊 Composition of the Universe:
| Component | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Dark Energy | 68% |
| Dark Matter | 27% |
| Normal Matter | 5% |
🧠 Summary
| Concept | What It Means |
|---|---|
| Light | Electromagnetic wave and particle |
| Bending of Light | Through refraction, lenses, gravity |
| Gravitational Lensing | Gravity bending light → space telescope effect |
| Dark Matter | Invisible matter that shapes the universe |
Leave a comment