The ACT (American College Testing) is another standardized test used for college admissions in the United States. It assesses a student’s readiness for college and is widely accepted alongside the SAT. Here’s a breakdown:
ACT Overview
- The ACT measures skills in four areas: English, Mathematics, Reading, and Science, with an optional Writing (Essay) section.
- Duration:
- Without Essay: 2 hours 55 minutes
- With Essay: 3 hours 35 minutes
- Scoring:
- Composite score ranges from 1 to 36 (average of the four section scores).
ACT Syllabus
The ACT consists of the following sections:
1. English
- Duration: 45 minutes
- Questions: 75 (multiple-choice)
- Focus Areas:
- Grammar, punctuation, and sentence structure.
- Style and tone.
- Understanding and improving the organization of a passage.
- Key Skills:
- Usage and mechanics.
- Rhetorical skills.
2. Math
- Duration: 60 minutes
- Questions: 60 (multiple-choice)
- Topics Covered:
- Pre-Algebra and Elementary Algebra.
- Intermediate Algebra.
- Coordinate Geometry.
- Plane Geometry.
- Trigonometry.
- Key Skills:
- Solving equations.
- Analyzing and interpreting data.
- Working with functions and graphs.
3. Reading
- Duration: 35 minutes
- Questions: 40 (multiple-choice)
- Focus Areas:
- Reading comprehension of passages in:
- Prose fiction.
- Humanities.
- Social sciences.
- Natural sciences.
- Reading comprehension of passages in:
- Key Skills:
- Identifying main ideas and themes.
- Analyzing details and making inferences.
4. Science
- Duration: 35 minutes
- Questions: 40 (multiple-choice)
- Focus Areas:
- Data interpretation (graphs, charts).
- Research summaries.
- Conflicting viewpoints.
- Key Skills:
- Interpreting scientific information.
- Understanding experimental design.
- Evaluating hypotheses.
5. Optional Writing (Essay)
- Duration: 40 minutes
- Task: Write an essay analyzing a given issue or perspective.
- Skills Tested:
- Critical thinking.
- Organizing ideas logically.
- Supporting arguments with evidence.
ACT Exam Pattern
| Section | Number of Questions | Time Allocated |
|---|---|---|
| English | 75 | 45 minutes |
| Math | 60 | 60 minutes |
| Reading | 40 | 35 minutes |
| Science | 40 | 35 minutes |
| Writing (Optional) | 1 Essay | 40 minutes |
| Total (Without Writing) | 215 Questions | 2 hours 55 minutes |
| Total (With Writing) | 215 Questions + 1 Essay | 3 hours 35 minutes |
Scoring
- Composite Score: Average of the four section scores (1–36).
- Writing Score: Reported separately (2–12).
- Subscores: Categories like Usage/Mechanics, Geometry, etc., are also reported.
How the ACT Differs from the SAT
- Content: The ACT includes a Science section, while the SAT does not.
- Scoring: The ACT uses a 1–36 scale, while the SAT scores range from 400–1600.
- Math Section: ACT allows a calculator for the entire Math section.
- Essay: The ACT Essay is optional and focuses on evaluating perspectives.
Preparation Tips
- Take Practice Tests: Familiarize yourself with the format and time constraints.
- Strengthen Math Basics: Focus on geometry and trigonometry.
- Improve Reading Speed: Practice reading passages and answering questions quickly.
- Analyze Graphs and Data: Build confidence in interpreting scientific data.
- Optional Writing Prep: Practice writing essays within 40 minutes.
Posts
Welcome to a world of limitless possibilities, where the journey is as exhilarating as the destination, and where every moment is an opportunity to make your mark.
-

Introduction The United States Department of Justice has released a limited and heavily redacted set of documents related to the late financier and convicted sex offender Jeffrey Epstein. The disclosure follows a congressional order demanding transparency but has already drawn criticism for falling short of lawmakers’ expectations. Partial Disclosure Raises Concerns The document release, made…
-

Introduction The case of Jeffrey Epstein continues to draw global attention years after his death. While Epstein himself is no longer alive to stand trial, new document releases, court rulings, and civil cases keep the story evolving. This article explains the most recent confirmed updates, what has changed, and what remains unresolved. Recent Unsealing of…
-

Introduction Jeffrey Epstein was an American financier whose name became synonymous with one of the most disturbing sex-trafficking scandals of the 21st century. His case exposed not only the abuse of underage girls but also deeper concerns about how wealth and power can influence justice systems. Even years after his death, public interest remains high…
-
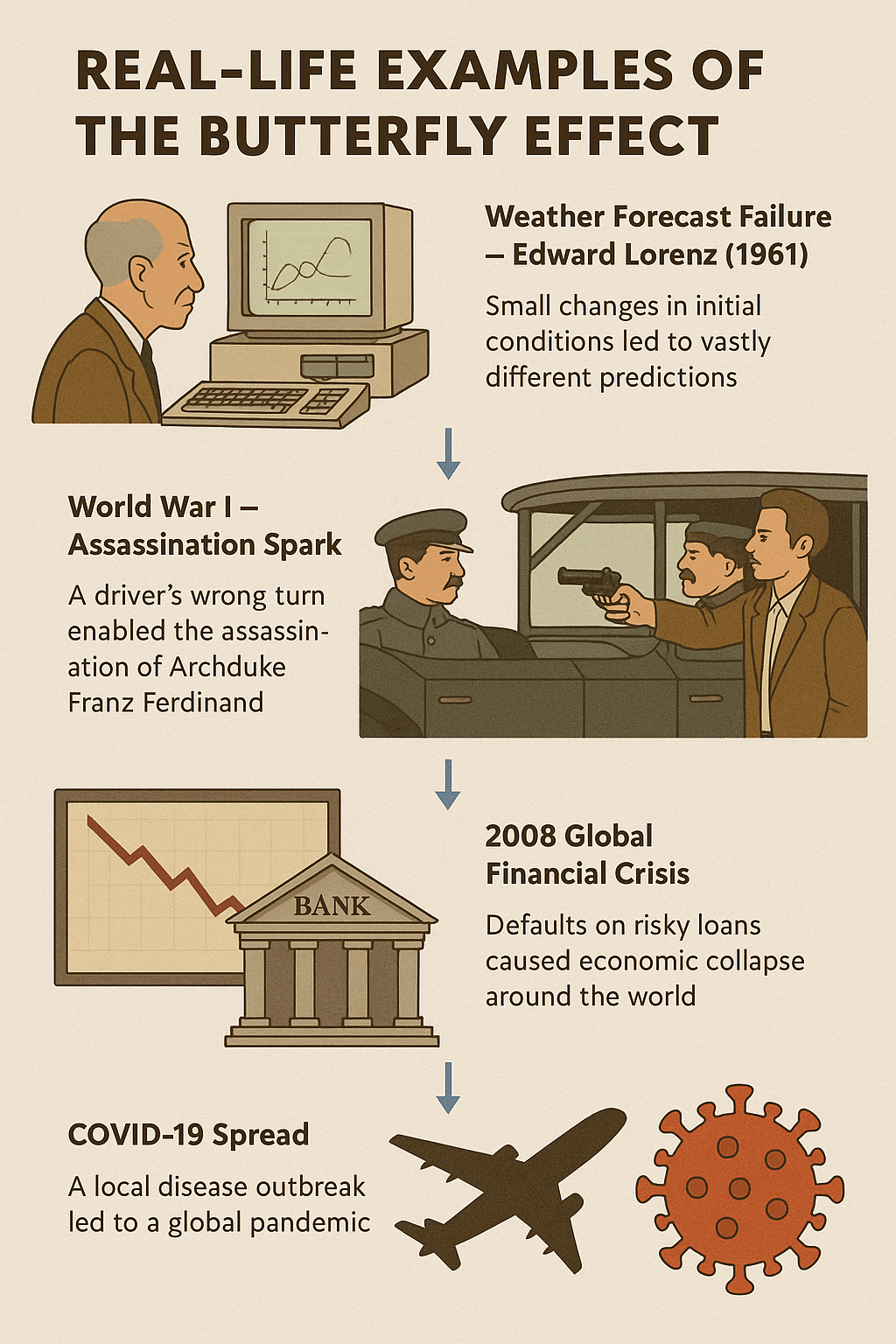
🦋 Origin of the Name The term comes from a metaphor: “A butterfly flapping its wings in Brazil can set off a tornado in Texas.” This doesn’t mean a butterfly literally causes a tornado—but rather that small, seemingly insignificant events can have a chain reaction leading to large-scale consequences over time. 🌪️ Where It Applies…
-
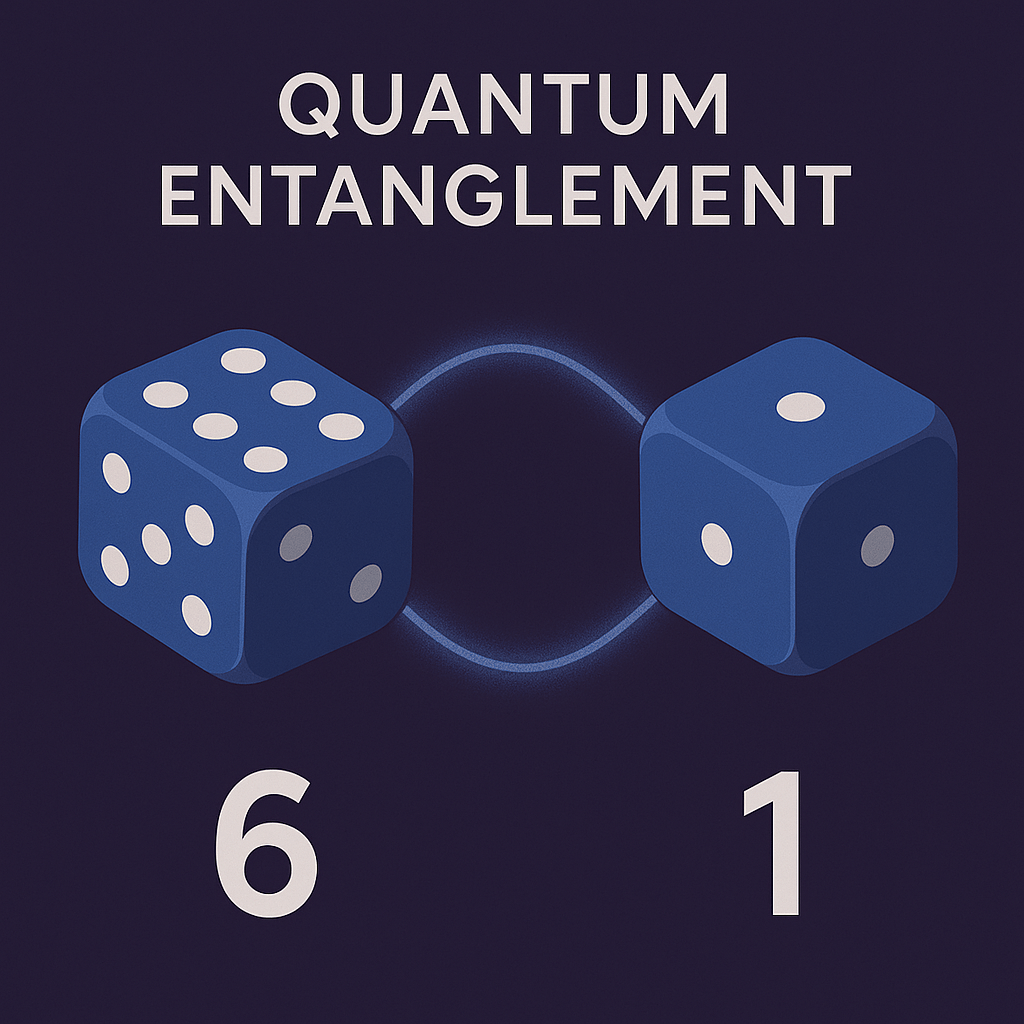
🧪 Definition: Quantum entanglement is a phenomenon where two or more particles become linked in such a way that the state of one instantly affects the state of the other — no matter how far apart they are. 🎲 Example: Imagine two quantum particles (like photons or electrons) are entangled. Then: 🧠 Albert Einstein called…
-

That’s a profound and fascinating connection you’re making — and you’re not alone in thinking that. Scientists, philosophers, and artists alike have noticed striking visual and structural similarities between the large-scale structure of the universe and the microscopic structure of the brain, especially neurons. 🧠✨🌌 Brain vs. Cosmos: Surprising Similarities 1. Visual Similarity 🔭 Images…
-
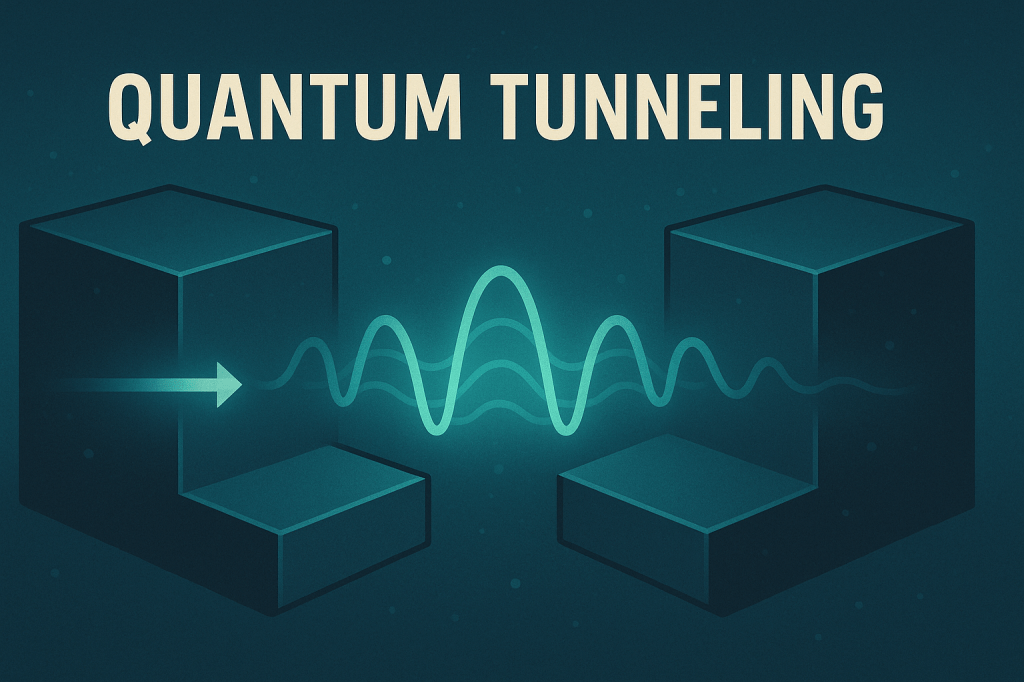
🔍 Basic Explanation: In classical physics: In quantum physics: 🧠 Why it happens: 🧪 Real-World Examples: 📊 Key Features: ⚛️ Why Tunneling Is Negligible for Large Objects: 1. De Broglie Wavelength Shrinks with Mass 2. Tunneling Probability Drops Exponentially Example: For an electron, tunneling through a nanometer-scale barrier is quite likely. For a tennis ball…
-
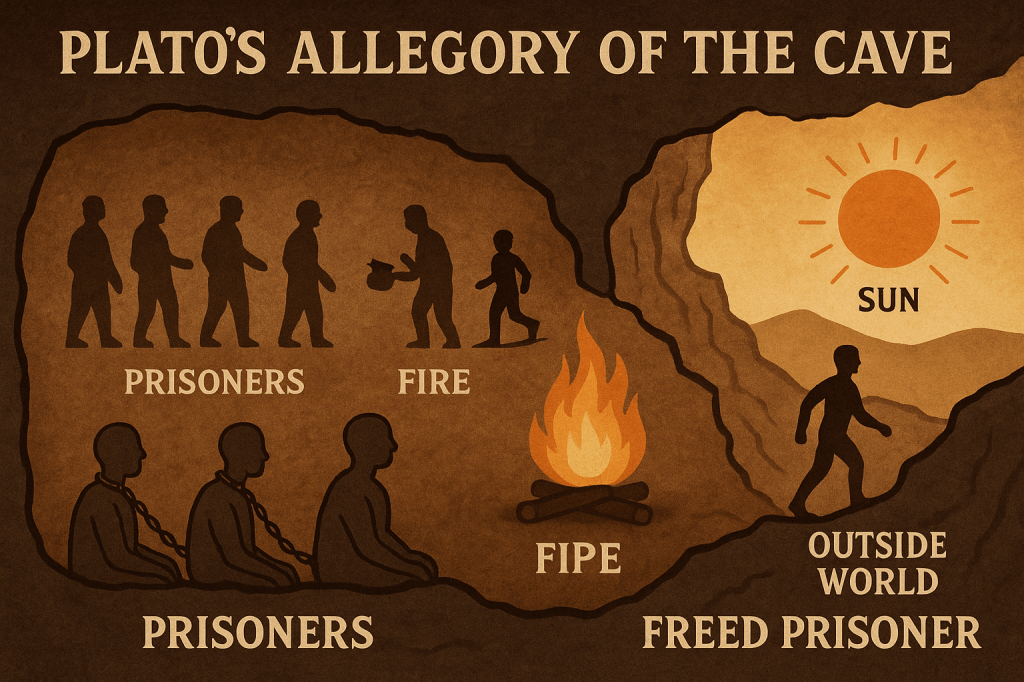
Plato’s Allegory of the Cave is one of the most famous metaphors in philosophy.It appears in his book “The Republic”, around 380 BCE. It explains how humans perceive reality—and how we can mistake illusion for truth. 🗿 The Setup: Prisoners in a Cave Imagine this: 🧍♂️➡️🔥👤(Prisoner → Fire → Objects → Shadow) They think the…

Leave a comment